1. Chemical Weed Killers
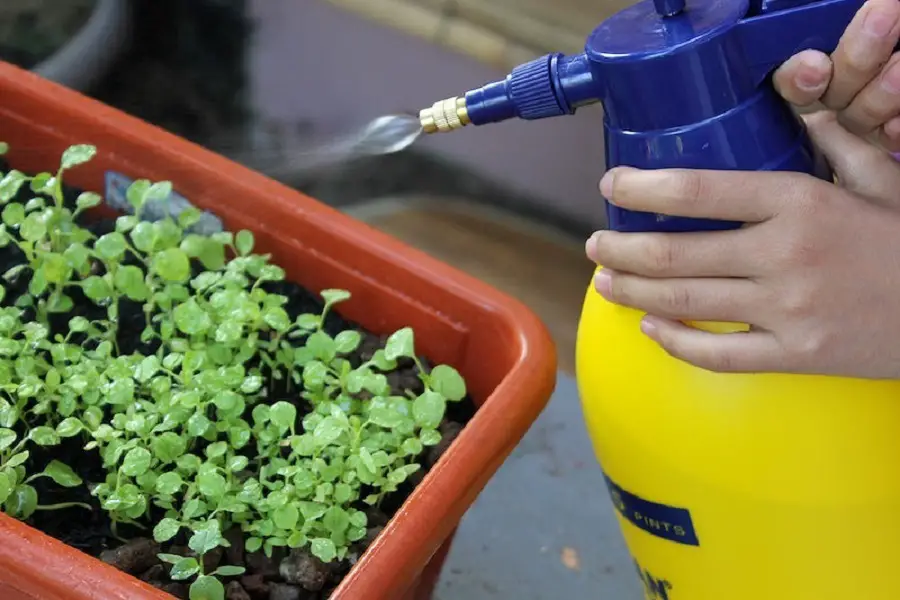

While effective at removing weeds, many chemical weed killers harm beneficial insects, soil health, and nearby plants. Opt for natural alternatives like vinegar-based sprays or manual weeding to protect your garden’s ecosystem.
2. Overused Mulch
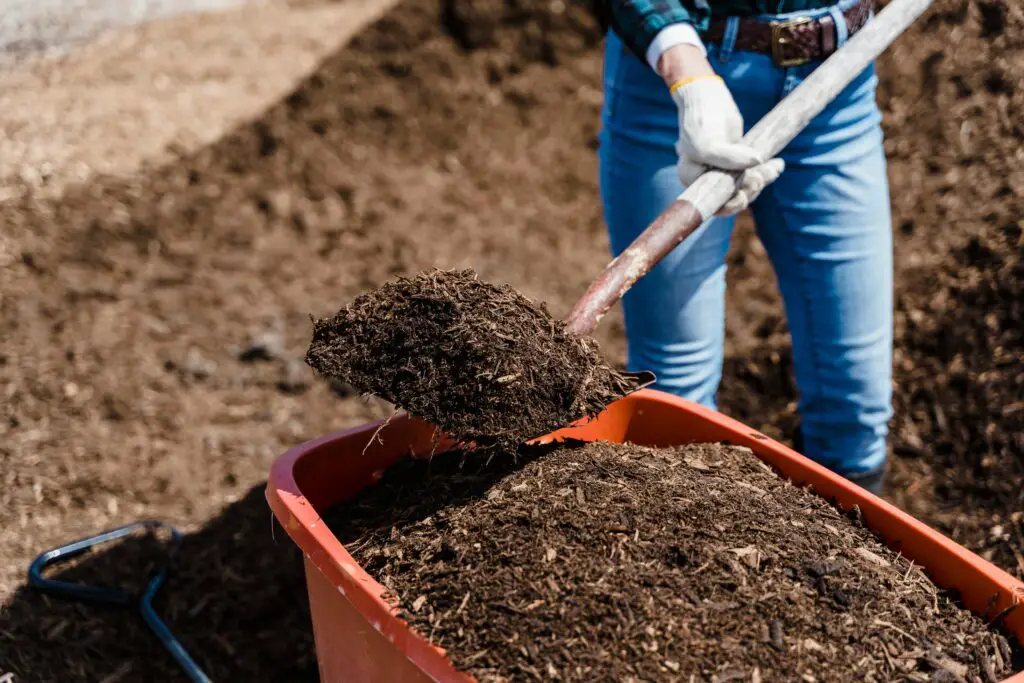

Too much mulch can suffocate plant roots, prevent water from reaching the soil, and attract pests. Stick to a thin layer (about 2-3 inches) of organic mulch to retain moisture without overdoing it.
3. Plastic Pots
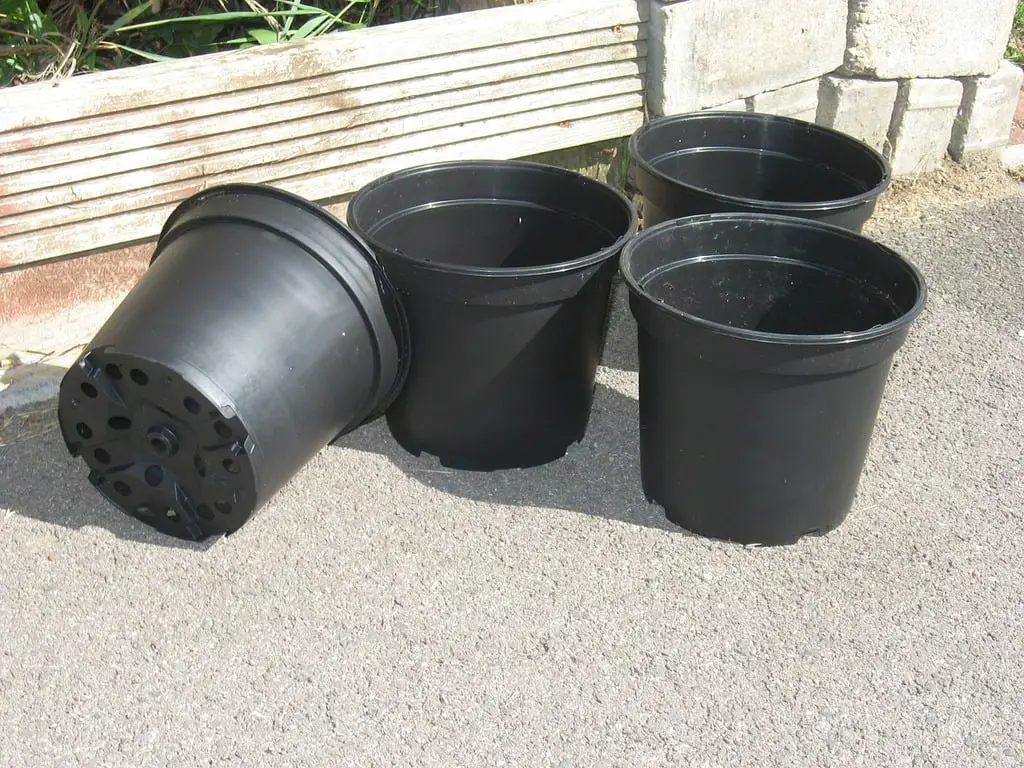

Non-biodegradable plastic pots left in gardens can leach chemicals into the soil over time. Consider switching to terracotta, ceramic, or biodegradable planters to maintain soil health and reduce waste.
4. Decorative Gravel
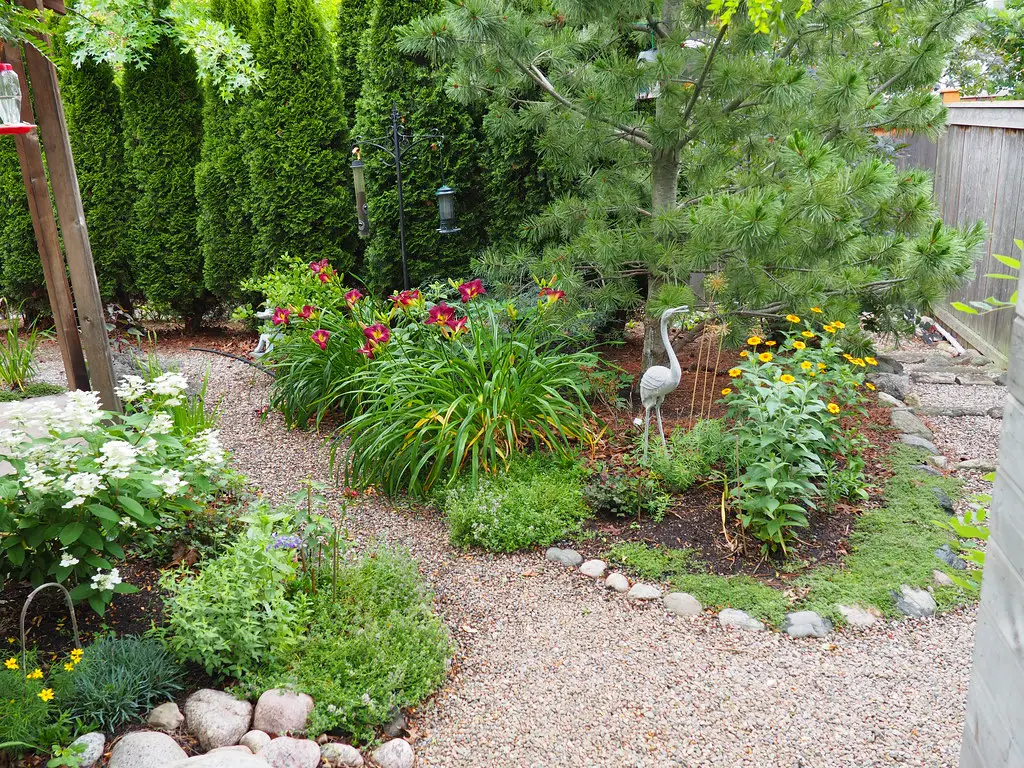

Gravel might look attractive, but it often heats up under the sun, raising the soil temperature and stressing nearby plants. Instead, use organic ground covers like bark or pine needles for a natural look and better plant health.
5. Unregulated Fertilizers

Overusing or choosing the wrong type of fertilizer can lead to chemical burn or imbalanced nutrients in your soil. Always test your soil first and use slow-release, organic fertilizers for optimal results.
6. Invasive Plants
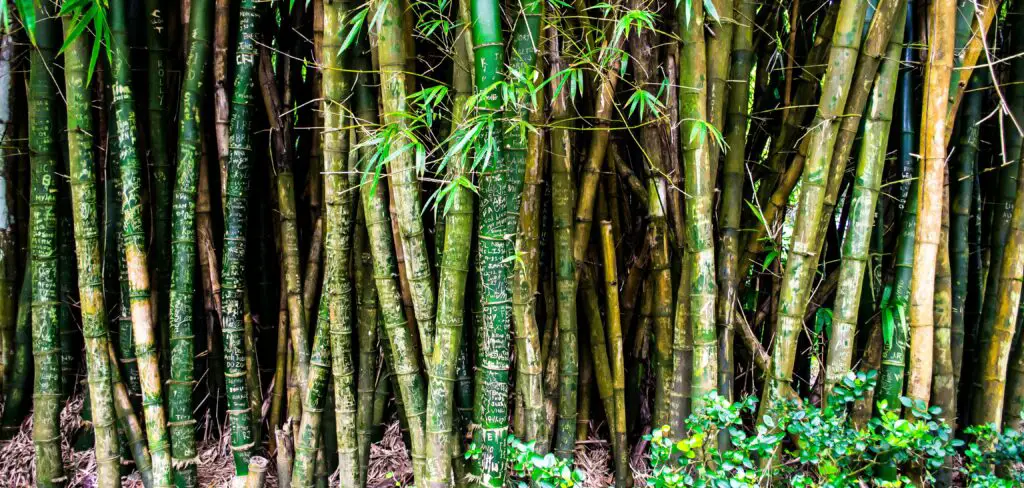

Planting species like mint or bamboo without proper containment can quickly overrun your garden and outcompete other plants. Use pots or barriers to keep these fast growers in check.
7. Bright Outdoor Lights
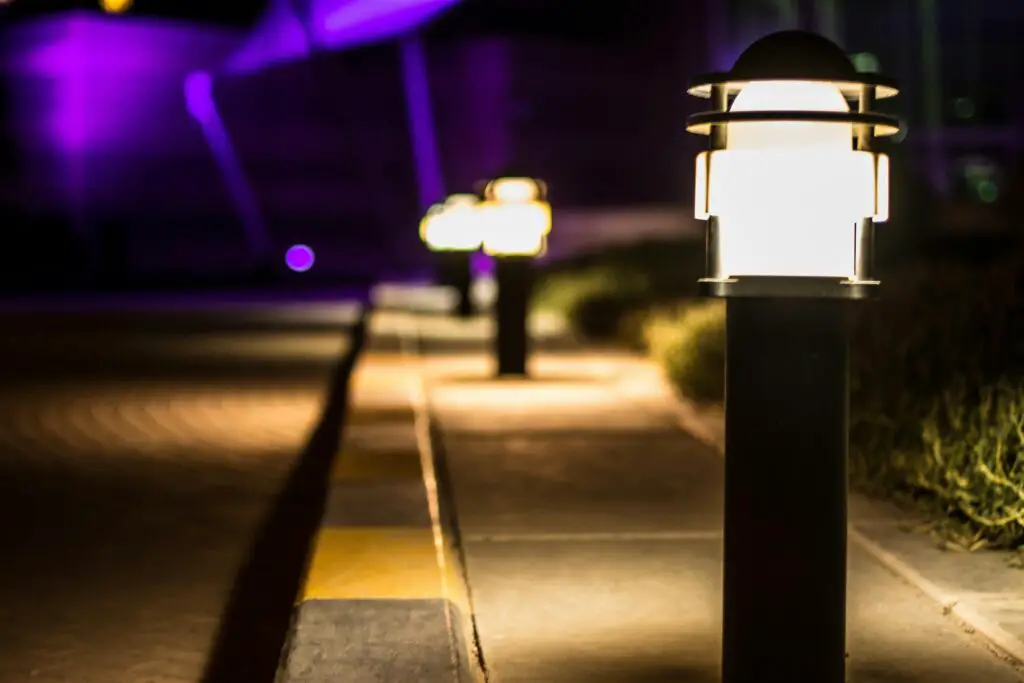

Excessive garden lighting can disrupt the natural cycles of pollinators and nocturnal wildlife. Opt for dim, motion-activated, or solar-powered lights to create a more wildlife-friendly space.
8. Painted Stones or Decorations
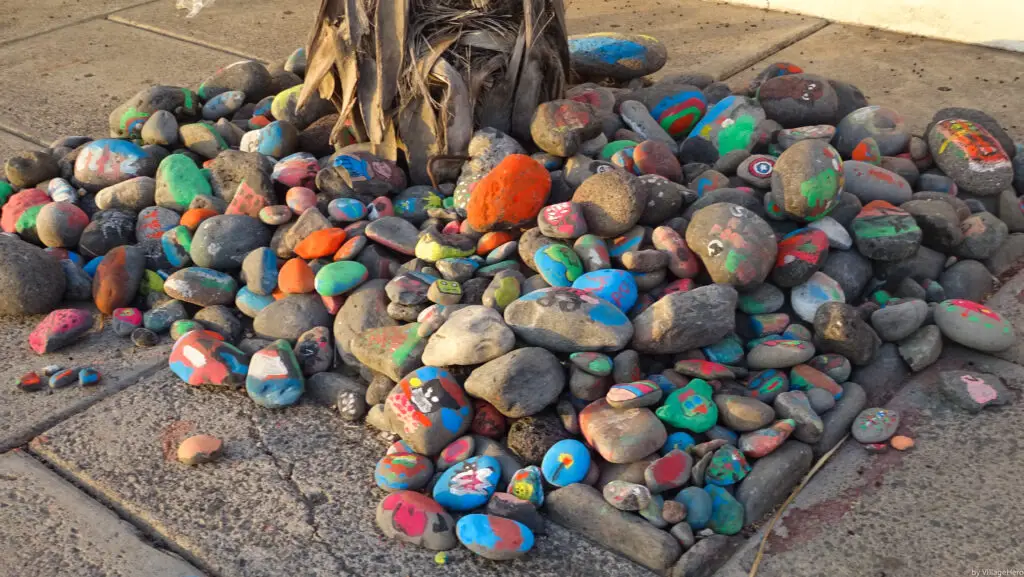
While charming, painted rocks or ornaments might contain harmful chemicals that leach into the soil, affecting plant growth. Stick to natural stones or untreated materials for garden decor.
9. Treated Wood
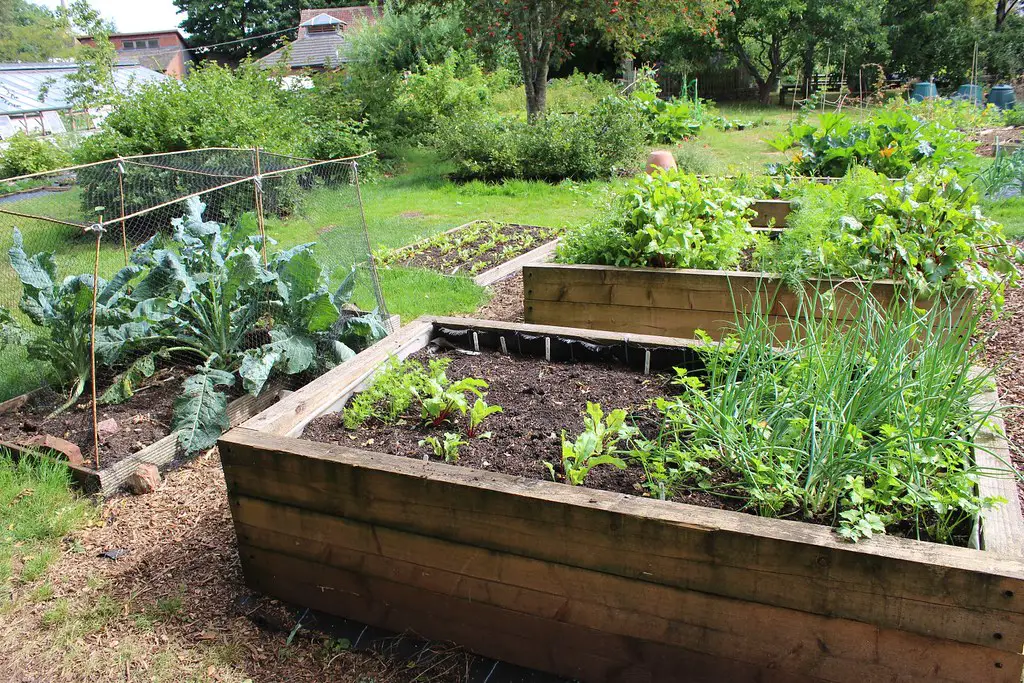

Pressure-treated wood used in raised beds or edging can release harmful chemicals into the soil. Instead, use untreated hardwoods or recycled materials like metal or stone for a safer garden environment.
10. Pesticides
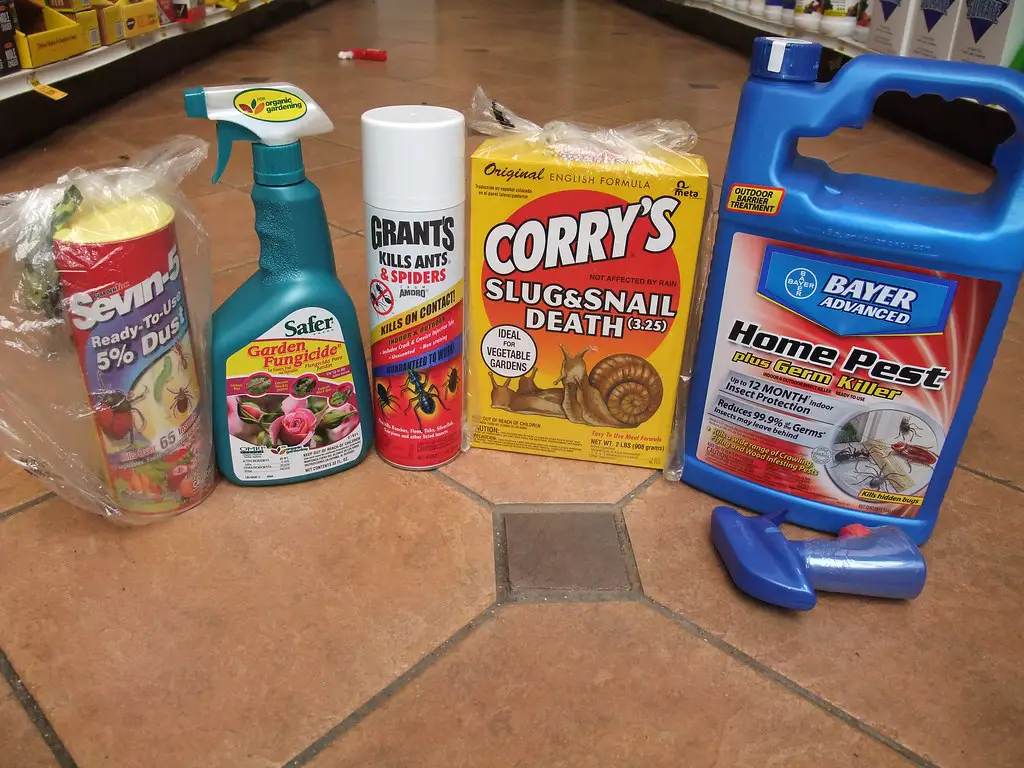

Non-selective pesticides not only kill harmful pests but also beneficial insects like bees and ladybugs. Switch to integrated pest management (IPM) techniques or natural deterrents like neem oil to protect your garden.
11. Compact Soil from Heavy Foot Traffic
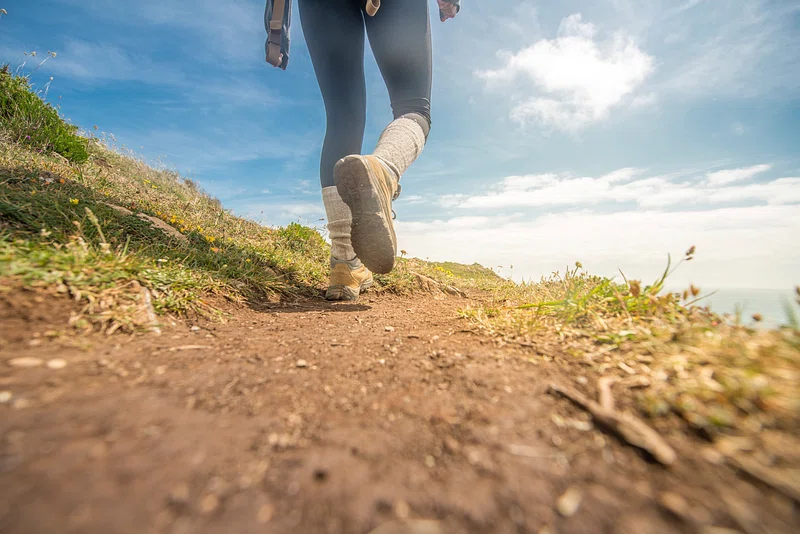

Walking repeatedly on garden paths can compact the soil, making it harder for plant roots to grow and water to penetrate. Use stepping stones or designated pathways to minimize damage.
12. Lawn Clippings with Chemicals
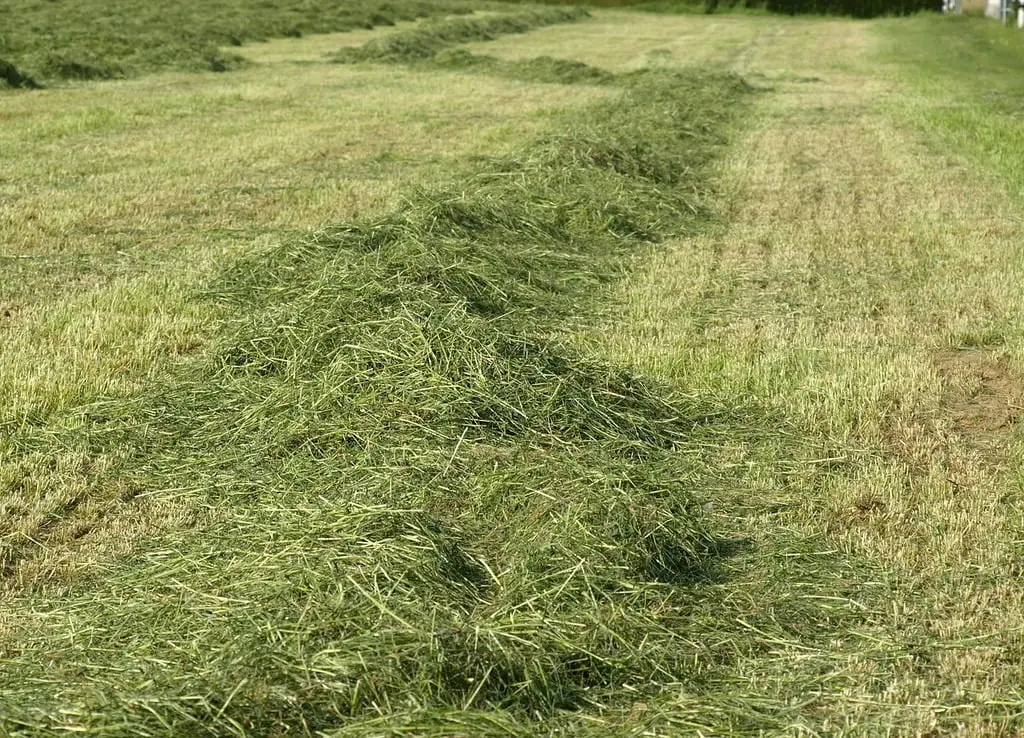

If your lawn is treated with herbicides or synthetic fertilizers, using its clippings as mulch can introduce toxins to your garden. Ensure clippings are chemical-free before using them as compost or mulch.
