Sustainability, innovation, and a touch of the unexpected are reshaping the construction world in 2025. As developers look for greener, stronger, and more cost-effective ways to build, they’re turning to materials that might surprise you—from mushrooms and seaweed to recycled denim and translucent wood. What once seemed unthinkable is now on job sites and blueprints around the world. These 14 strange building materials are pushing the boundaries of architecture and changing the way our homes and cities are made.
1. Recycled Plastic Bricks
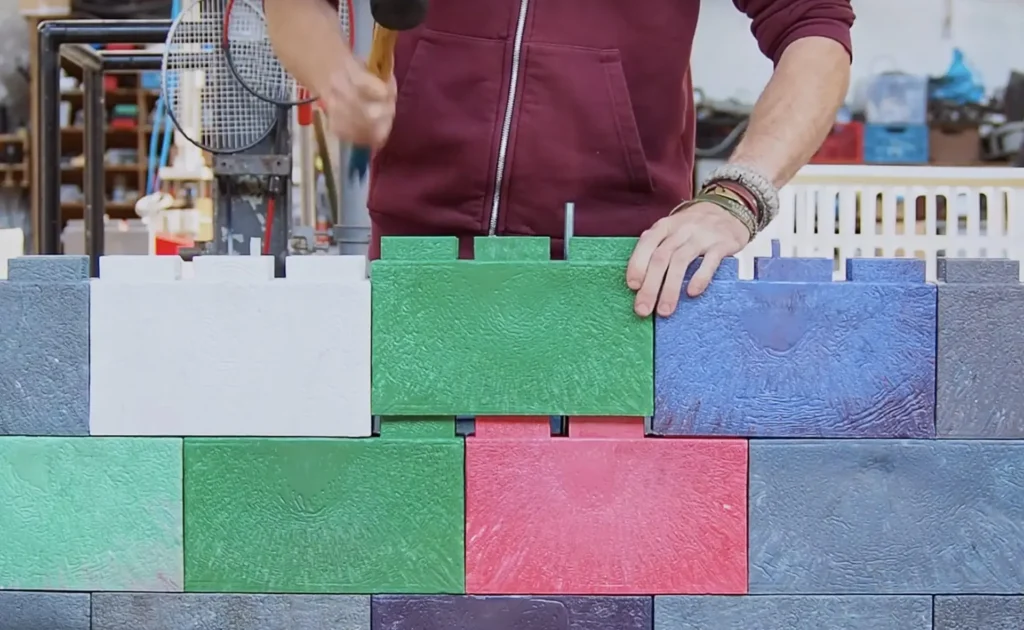
Recycling plastic waste into durable construction materials has become a cutting-edge solution to both waste management and building needs. Recycled plastic bricks are made by transforming discarded plastic into strong, modular components that can be used in construction. These bricks are particularly advantageous in regions overwhelmed with plastic pollution, as they help reduce waste while providing a sustainable building material. The resulting bricks are lightweight, weather-resistant, and durable, which makes them ideal for a variety of applications, from housing to public infrastructure.
By using recycled plastic, these bricks also help divert millions of tons of plastic waste from landfills each year. In addition to their environmental benefits, they are highly customizable, offering versatility in design. Research indicates that plastic-based bricks could be used to build homes more affordably and efficiently, especially in low-income areas. The material’s resistance to water and pests further enhances its appeal for construction in diverse environments. Builders can also benefit from the energy savings associated with the manufacturing of these bricks, which are produced using less energy than traditional materials. Companies like Plastic Bank are pioneering this process by collecting ocean-bound plastic waste to turn into building materials, making their products both eco-friendly and socially responsible.
2. Mushroom Mycelium
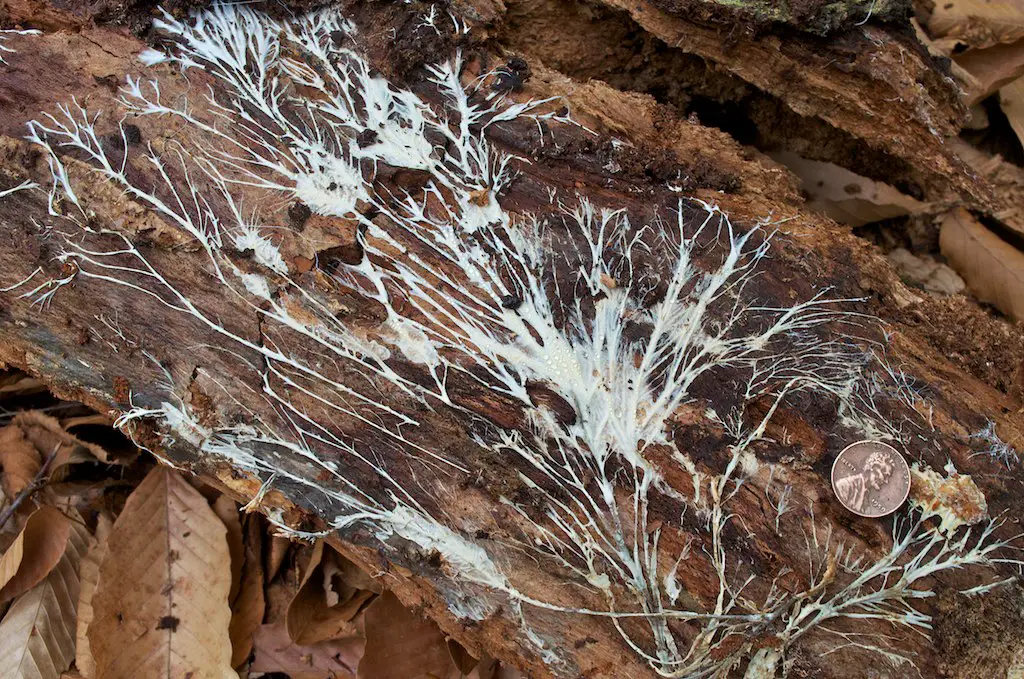

Mushroom mycelium, the root-like network of fungal cells, has emerged as an innovative alternative to conventional building materials like insulation. It is incredibly lightweight, highly biodegradable, and possesses impressive thermal insulating properties. Mycelium-based insulation has been shown to be effective in controlling indoor temperature while having minimal environmental impact. This material’s sustainability extends beyond insulation; researchers are also experimenting with it for creating furniture, interior panels, and even construction blocks.
The fact that it is entirely natural and grows rapidly makes it an appealing choice for eco-friendly projects. Additionally, mycelium can be grown into custom shapes and sizes, offering flexibility in design. This fungal-based material also has fire-resistant qualities, enhancing safety in buildings. Due to its biodegradability, it is an excellent choice for reducing long-term waste. According to The New York Times, mycelium has the potential to revolutionize the construction industry by providing an alternative that can be grown rather than manufactured in factories. As it gains traction, it may well be a key player in sustainable architecture.
3. Transparent Wood
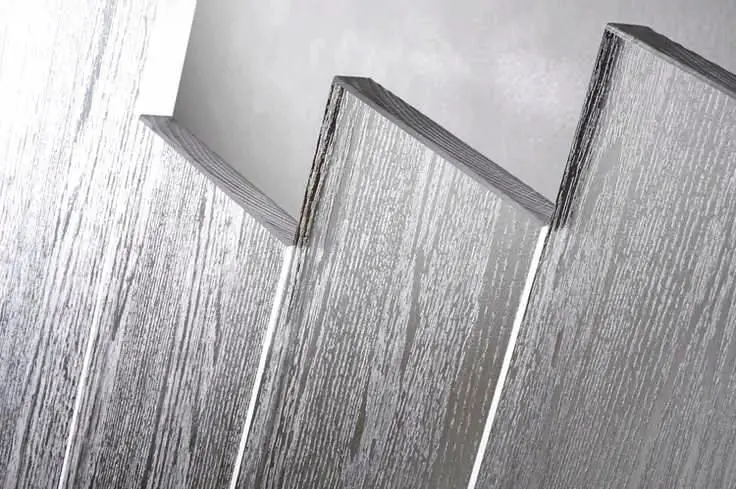

Transparent wood is a revolutionary material that has gained attention as a sustainable alternative to glass in modern architecture. This material is created by removing the natural pigments from wood through a chemical process, leaving behind a clear, strong, and insulating material. Unlike glass, transparent wood is not only lightweight but also provides superior thermal insulation, which makes it an energy-efficient choice for windows, skylights, and facades. The material allows for natural light to enter while reducing glare, offering a softer light compared to glass.
Additionally, transparent wood is far stronger and more durable than glass, making it a safer option in construction. Its ability to retain the natural texture of wood also gives it a unique aesthetic appeal, merging the benefits of glass with the warmth of wood. Researchers at Harvard University have made significant advances in enhancing its transparency and durability, allowing for broader applications. With ongoing innovations, transparent wood is poised to play a significant role in sustainable architecture. It can help reduce energy consumption by minimizing heat loss through windows, making buildings more energy-efficient. This material offers a glimpse into the future of eco-friendly, high-performance construction.
4. Carbon-Negative Concrete
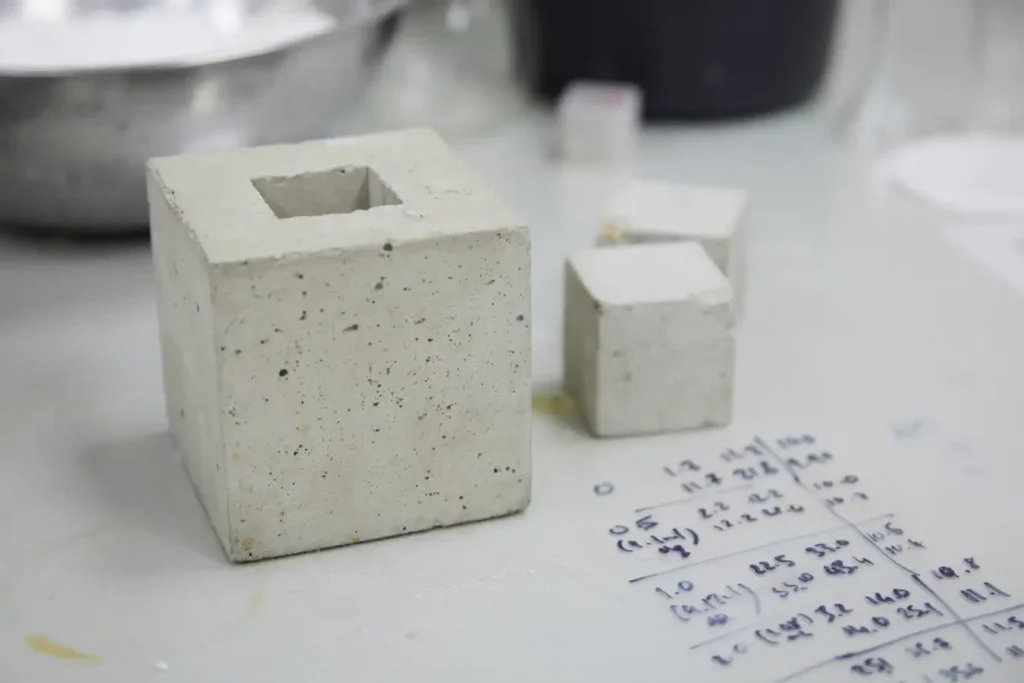

Concrete is one of the most widely used construction materials, but it is also a major contributor to global carbon emissions due to its production process. Carbon-negative concrete offers a game-changing solution by not only reducing emissions but actively absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere during its curing process. This innovative material helps offset the environmental footprint of traditional concrete, which is responsible for approximately 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. The process of making carbon-negative concrete involves incorporating waste materials like industrial byproducts and carbon-capturing technologies that promote carbon sequestration.
The end result is a highly durable material that retains the strength and longevity of regular concrete but with a significantly reduced environmental impact. According to The Guardian, several companies are already scaling up the production of this sustainable alternative. This technology could drastically shift the construction industry toward a more sustainable future. Carbon-negative concrete not only helps mitigate climate change but also encourages the recycling of waste materials that would otherwise end up in landfills. By using this material in large-scale projects, builders can significantly lower the carbon footprint of new buildings. This breakthrough provides a promising avenue for sustainable urban development.
5. Recycled Denim Insulation

Recycled denim insulation is an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative to traditional fiberglass insulation. This innovative material is made by repurposing old jeans and denim scraps, which would otherwise contribute to landfill waste. Not only does denim insulation offer excellent thermal properties, but it is also an effective soundproofing material. Its natural fibers make it a safer option to handle compared to fiberglass, which can cause skin irritation during installation. Denim insulation is biodegradable, so it won’t linger in landfills long after it has been used. Additionally, it’s non-toxic, making it an attractive choice for green buildings.
Unlike conventional insulation materials, recycled denim is made using less energy in the manufacturing process, further reducing its environmental impact. It has also been recognized for its energy efficiency in controlling heating and cooling costs, which adds to its appeal for homeowners and builders alike. Recycled denim insulation is growing in popularity due to its ability to improve indoor air quality and sustainability. According to TreeHugger, denim insulation is quickly becoming a favorite for those aiming to build homes that are both comfortable and environmentally responsible.
6. Solar-Activated Paint

Solar-activated paint is one of the most innovative advancements in energy-efficient building materials. This special type of paint is designed to convert sunlight into electricity, turning any surface coated with it into a mini solar panel. Solar-activated paint can be applied to rooftops, walls, and windows to help generate clean energy and reduce reliance on traditional power sources. It works by incorporating photovoltaic compounds that harness solar energy and convert it into usable electricity. This paint can contribute to a building’s energy needs, lowering utility costs while reducing its carbon footprint.
While still in the early stages of development, solar-activated paint has the potential to be an affordable and easy-to-apply solution for creating self-sustaining buildings. Developers are exploring its use for both residential and commercial buildings to make them more energy-efficient. The adaptability of this technology makes it a promising tool for enhancing the sustainability of structures without requiring major renovations. This eco-friendly alternative could play a key role in reducing the environmental impact of the construction industry. Solar-activated paint is one of the most exciting developments in renewable energy, as it promises to revolutionize the way we think about energy generation in buildings.
7. Hempcrete

Hempcrete is an innovative building material that is made by combining hemp fibers with lime-based binders to create a lightweight, fire-resistant, and highly insulating product. It is becoming an increasingly popular choice for eco-friendly building projects due to its carbon-negative properties. Hemp absorbs CO₂ as it grows, making it a sustainable resource for construction. Unlike traditional concrete, hempcrete is breathable, helping regulate humidity and improving indoor air quality.
This material is also non-toxic, making it safer to handle and live in than conventional building materials. Hempcrete’s insulating qualities make it an excellent option for creating energy-efficient buildings, helping to reduce heating and cooling costs. It is also pest-resistant, which further extends the lifespan of structures built with it. As the demand for sustainable building materials increases, hempcrete is gaining traction among architects and builders who prioritize environmental impact. This material is ideal for use in both residential and commercial projects due to its sustainability and versatility. Hempcrete offers a unique solution for creating buildings that are both eco-friendly and cost-effective.
8. Bamboo Reinforcements
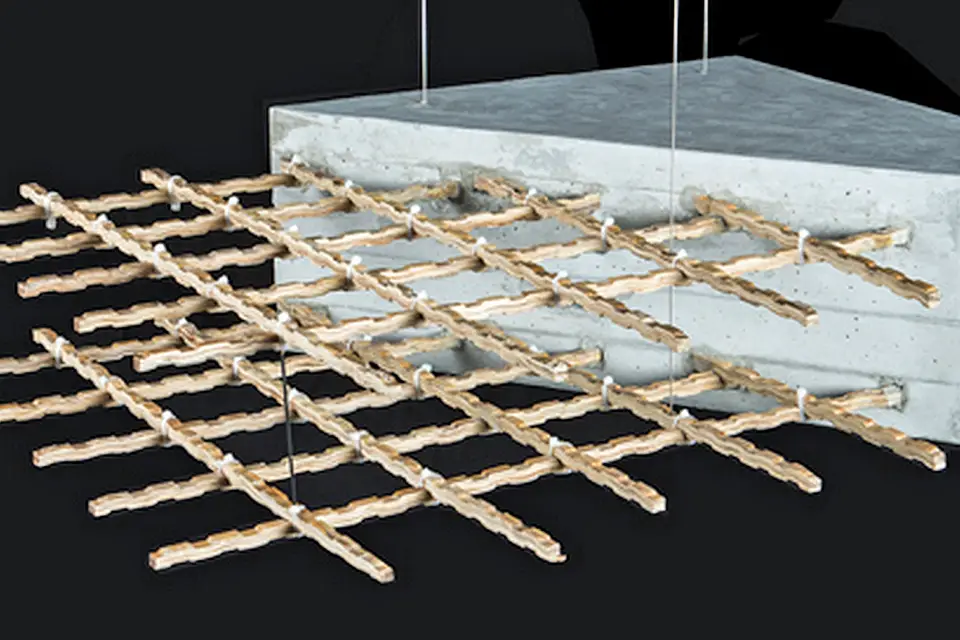

Bamboo is emerging as a viable and sustainable alternative to steel for reinforcing concrete in construction. Known for its rapid growth and high strength-to-weight ratio, bamboo is a renewable resource that can help reduce the reliance on non-renewable materials in the construction industry. Bamboo’s flexibility and strength make it an ideal reinforcement material for concrete structures, especially in regions prone to earthquakes or other natural disasters. Unlike steel, bamboo requires minimal processing and has a lower carbon footprint, making it a more sustainable option. Bamboo can also be harvested every few years, unlike traditional timber, which can take decades to mature.
This plant-based material can be used for beams, columns, and other structural elements, offering a more sustainable way to reinforce concrete. Bamboo’s rapid regrowth and minimal environmental impact make it a perfect fit for eco-conscious developments. With its strength and sustainability, bamboo is set to become a key material in the next generation of green building projects. Bamboo reinforcements have the potential to transform the construction industry by offering an alternative that is both strong and environmentally responsible.
9. Air-Purifying Concrete

Air-purifying concrete is an innovative material that goes beyond its structural capabilities by actively improving air quality. This concrete is embedded with photocatalytic compounds that help break down pollutants when exposed to sunlight. These compounds facilitate chemical reactions that convert harmful pollutants into harmless substances, reducing the levels of smog and particulate matter in the air. Air-purifying concrete is especially beneficial in urban areas, where air quality is often compromised by high levels of pollution.
This material has the potential to contribute to cleaner, healthier cities by actively filtering the air surrounding buildings. Its ability to purify the air is achieved without sacrificing the durability or strength of traditional concrete, making it a promising option for both new and retrofitted buildings. This innovative material could also help reduce the need for expensive air purification systems, making cities more sustainable in the long run. Air-purifying concrete could be the future of urban development, where construction materials not only support the physical structure of buildings but also contribute to the health of the environment.
10. Recycled Glass Tiles

Recycled glass tiles are rapidly becoming a popular choice for modern, eco-friendly interior design. Made from crushed glass bottles and other glass waste, these tiles offer a sustainable alternative to traditional ceramic or stone tiles. Not only do they help reduce landfill waste, but they are also highly durable and visually striking. The tiles can be used in a wide variety of applications, from kitchen backsplashes to bathroom walls and floors. Recycled glass tiles are available in a range of colors and finishes, allowing homeowners and designers to create unique, vibrant designs.
They are also easy to maintain and resistant to staining, making them a practical choice for high-traffic areas. These tiles also reflect light, creating a sense of space and brightness in rooms. Recycled glass tiles are also non-toxic, making them a safer choice for families and the environment. By choosing these tiles, builders and homeowners can contribute to sustainability efforts while adding a modern touch to their spaces.
11. Bioplastic Panels
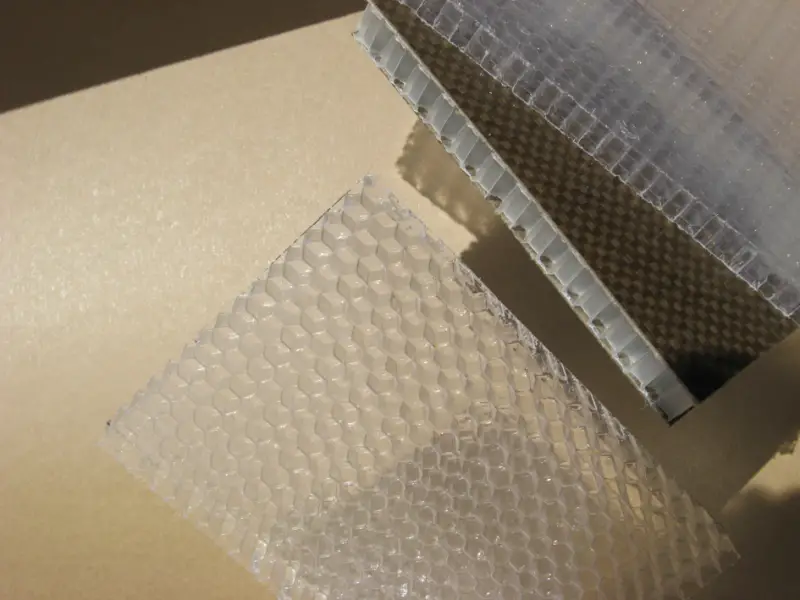

Bioplastics, derived from renewable plant-based sources, are becoming a popular alternative to conventional petroleum-based plastics in the construction industry. These bioplastic panels are used in applications ranging from cladding and furniture to decorative elements, offering a sustainable solution for eco-conscious architects and builders. Unlike traditional plastics, bioplastics are biodegradable and can be recycled, helping to reduce the environmental burden of construction projects. This innovative material offers the flexibility and durability of plastic while minimizing the use of fossil fuels.
As environmental concerns continue to rise, industries across the world are seeking alternatives to traditional plastic, and bioplastic panels are gaining traction as a greener choice. Moreover, bioplastics made from crops like corn, sugarcane, or cellulose provide a carbon-neutral option since the plants absorb carbon dioxide while growing. Not only are bioplastics better for the environment, but they can also contribute to improving indoor air quality by offering lower levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Leading researchers suggest that bioplastics may soon become more affordable as production processes evolve, increasing their availability and use in large-scale construction projects.
12. Papercrete

Papercrete is a unique and innovative building material that combines recycled paper with cement to create a lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional construction materials. The main advantage of papercrete lies in its use of waste paper, significantly reducing landfill waste while offering a low-cost solution for building projects. This material can be molded into various shapes for use in walls, roofing, and insulation, making it especially popular in small-scale and sustainable construction projects. Not only does papercrete provide insulation and structural integrity, but it also has a low environmental impact due to its reliance on recycled materials. The production process of papercrete consumes less energy than the creation of conventional concrete, contributing to its sustainability credentials.
Furthermore, because papercrete is highly porous, it provides natural soundproofing properties, making it an excellent choice for residential buildings and noise-sensitive environments. As construction methods continue to evolve, papercrete is being increasingly explored as a viable material for eco-friendly homes, particularly those seeking to lower their carbon footprint. Some studies have shown that the carbon footprint of papercrete is significantly lower than that of traditional building materials, particularly when the paper is sourced from recycled materials.
13. Algae-Based Bioplastics
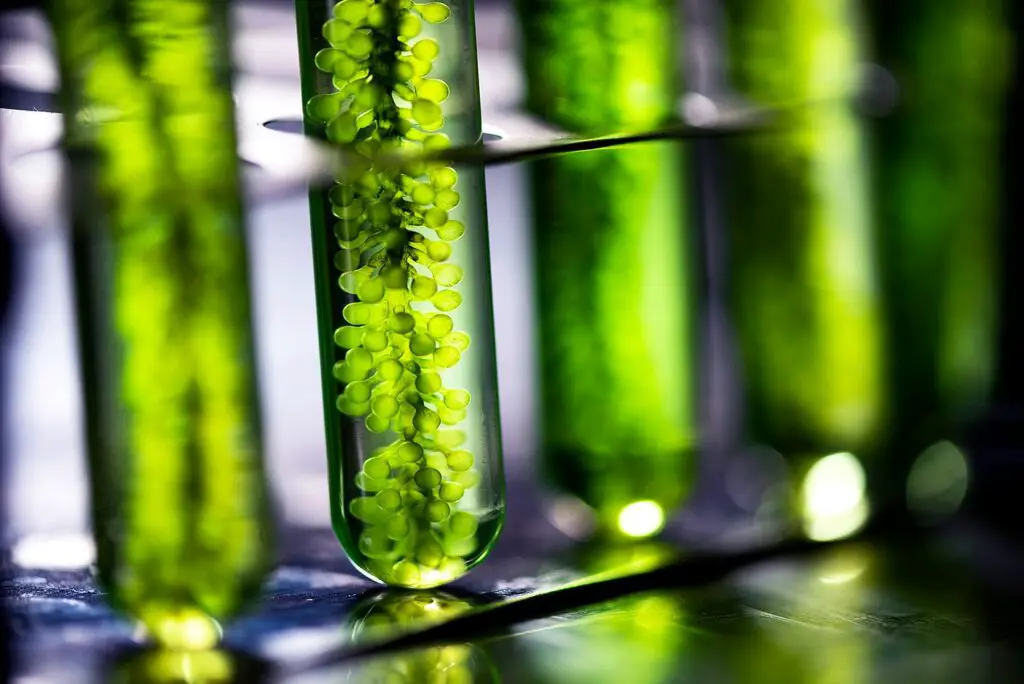

Algae-based bioplastics are a cutting-edge development in the world of sustainable construction. Derived from algae, these bioplastics offer a biodegradable, renewable alternative to petroleum-based plastics used in traditional building materials. Algae is a versatile raw material, and bioplastics made from it can be molded into various shapes, making them ideal for applications such as wall panels, fixtures, and decorative elements. Unlike petroleum-based plastics, algae bioplastics break down naturally over time, minimizing their environmental impact when they reach the end of their life cycle.
These bioplastics not only reduce the environmental impact of construction but also have the potential to absorb carbon dioxide during their growth phase, making them a carbon-negative material. Research into algae-based bioplastics has gained significant momentum, with promising results indicating that they could replace conventional plastics in many sectors. As the demand for sustainable construction materials increases, algae-based plastics could become a critical component of green building practices. By using algae, builders can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels while still achieving high-performance, durable materials.
14. 3D-Printed Earth
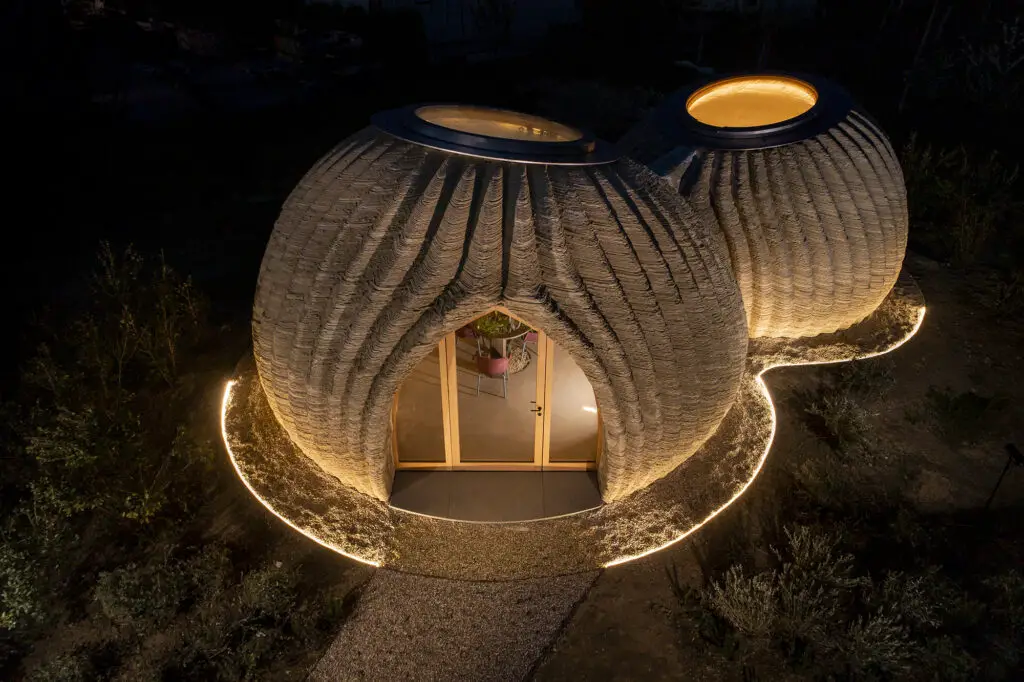

The combination of 3D printing technology with natural materials such as soil and clay has paved the way for an innovative approach to sustainable construction. Known as 3D-printed earth, this method involves using 3D printing techniques to create structures from earth-based materials, offering an affordable, environmentally-friendly option for building homes and other infrastructure. The use of local soil not only cuts down on transportation emissions but also creates structures that blend seamlessly into their natural environment. This method of construction is highly adaptable, allowing for intricate, organic shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional building techniques. 3D printing also minimizes material waste, as the precise nature of the process ensures that only the necessary amount of material is used.
Additionally, 3D-printed earth structures often have superior thermal insulation properties, making them ideal for climates where energy efficiency is a top priority. The scalability of 3D printing allows for the construction of low-cost homes, particularly in areas with limited access to traditional building materials, providing a solution to housing shortages. This technology is gaining interest for its potential to revolutionize affordable housing in developing countries and disaster-stricken areas, where speed and cost are crucial factors.
