1. Touchscreens Replacing Physical Controls

Car dashboards and home appliances increasingly use touchscreens instead of knobs and buttons. The reason was flexibility and a cleaner design that could be updated with software. In practice, flat glass removes tactile feedback that once guided your hands without looking. Simple actions like adjusting volume or temperature now demand visual attention.
This made daily interactions less intuitive because humans rely heavily on muscle memory. Physical controls communicate function through shape, resistance, and placement. Touchscreens hide those cues behind identical icons and menus. The automation prioritizes aesthetic and software efficiency over embodied understanding.
2. Autocorrect and Predictive Text

Autocorrect was designed to reduce typing errors and speed up communication. It uses dictionaries and language models to guess what you meant to type. However, it often replaces correct but uncommon words with more frequent ones. This forces users to constantly monitor and correct the automation.
The intuition problem comes from losing control over language output. You type something deliberately, but the system silently changes it. Over time, people adapt by typing differently to avoid triggering errors. Instead of writing naturally, users write defensively.
3. Algorithmic Social Media Feeds

Social platforms shifted from chronological feeds to algorithmic ones to increase engagement. These systems automatically prioritize content based on predicted interest. As a result, users no longer understand why they are seeing specific posts. The mental model of “newest updates first” quietly disappeared.
This makes daily browsing less intuitive because cause and effect are obscured. Liking one post can influence your feed for weeks without clear feedback. You cannot easily predict how an action will shape future content. The automation replaces transparency with optimization.
4. Smart Thermostats

Smart thermostats automate heating and cooling to save energy. They learn patterns from user behavior and sensor data. Over time, they may change temperatures without explicit input. Users often find rooms warmer or colder than expected.
The intuition gap appears when manual adjustments stop behaving consistently. Turning the temperature up does not always lead to immediate or lasting changes. The system may override you later based on learned behavior. Control becomes indirect and delayed.
5. Keyless Car Entry Systems

Keyless entry systems automatically unlock cars when the fob is nearby. The goal was convenience and reduced physical effort. However, drivers can no longer clearly tell when the car is locked. This has led to frequent accidental unlocks.
Intuitively, locking something used to require a deliberate action. Now the car decides based on proximity and timing. Users must trust invisible rules rather than physical confirmation. The automation removes a clear moment of certainty.
6. Automatic Software Updates

Operating systems and apps now update automatically in the background. This reduces security risks and maintenance effort for users. The downside is sudden interface or behavior changes. Features move or disappear without warning.
This erodes intuition because familiarity is repeatedly disrupted. Learned workflows stop working overnight. Users must relearn tasks they already mastered. The automation assumes progress is always welcome.
7. GPS Navigation for Everyday Routes
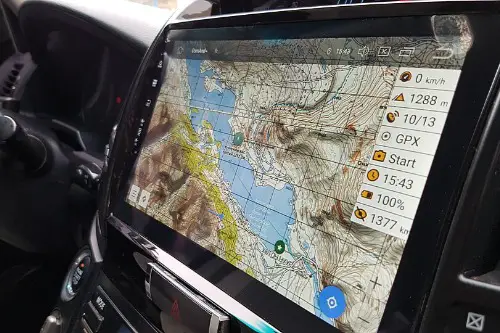
GPS navigation automates route planning using real-time data. It is especially useful in unfamiliar areas. However, many people now rely on it for routine trips. Over time, spatial awareness declines.
The intuition loss shows up when technology fails. Without GPS, some drivers cannot describe or visualize their route. They followed instructions rather than forming a mental map. Automation replaced understanding with compliance.
8. Auto-Save and Cloud Syncing

Auto-save and cloud syncing prevent data loss by saving continuously. This removed the need for manual saving. However, it also removed clear states of completion. Users are often unsure what version is current.
Intuitively, saving used to mark a deliberate checkpoint. Now changes propagate instantly across devices. Mistakes sync just as efficiently as good edits. The automation blurs the line between draft and final.
9. Streaming Platform Autoplay
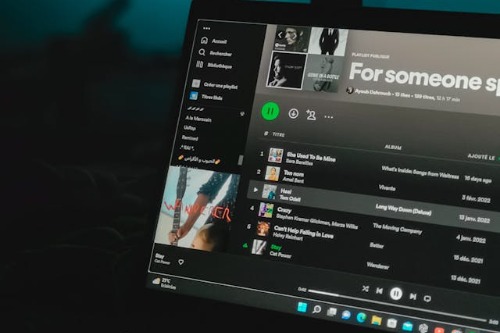
Autoplay automatically starts the next episode or video. It was introduced to reduce friction and keep viewers engaged. The system decides what comes next and when. Stopping requires active intervention.
This disrupts intuitive stopping points. Episodes once ended with a natural pause for reflection or choice. Autoplay removes that moment by default. The automation nudges behavior without explicit consent.
10. Automatic Headlights and Wipers

Cars now commonly automate headlights and windshield wipers. Sensors decide when conditions warrant activation. While convenient, these systems are not always accurate. Drivers may not notice failures immediately.
The intuition problem arises from reduced situational checking. Drivers stop thinking about visibility as an active responsibility. When automation misjudges conditions, reaction time increases. Awareness is replaced by assumption.
11. Voice Assistants for Simple Tasks

Voice assistants automate tasks like setting timers or checking the weather. They reduce the need for menus and screens. However, they require remembering specific phrasing. Slight variations can cause failure.
This makes interaction less intuitive than physical actions. Turning a knob has infinite acceptable variations. Voice commands are brittle and constrained. Users adapt to the system instead of the system adapting to them.
12. Automated Customer Service Systems

Automated phone trees and chatbots handle routine customer service. They reduce costs and scale easily. However, they force users into predefined paths. Unusual problems are hard to express.
The intuition breakdown happens when human conversation rules no longer apply. Explaining context or nuance becomes difficult. Users must guess which option best fits their issue. The automation optimizes efficiency at the expense of understanding.
This post 12 Automation Choices That Made Daily Life Less Intuitive was first published on Greenhouse Black.
